What is a Noun? How to use it?

The Noun
The parts of speech in the English language are nouns, pronouns, numerals, adjectives, verbs, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. A part of speech describes the function a word plays in a sentence.
A Noun is a part of speech that is used to name a person, a thing, a place, or an idea in a sentence.
Most sentences contain a noun. There are a few sentences without a noun. Nouns answer the following 2 questions:
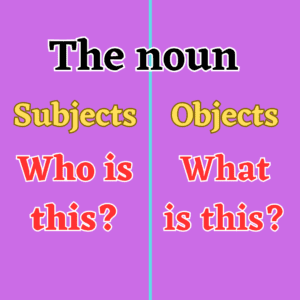
Who is this? A girl, a man, an engineer
What is this? A house, wheat, darkness, and work
The Noun is used with an article (definite or indefinite):
There is a book on the table (indefinite article).
The book that is on the table is very interesting (definite article).
The Noun is also used with prepositions, such as:
on the table, under the table, in the box, to the house, behind the house, near the house, in front of the house, into the room, against the will, inside the heart, by pen, by mail, with a knife, for three days, up the stairs, before the war, after dinner, at a factory, about the trip
I go to school every day. My father works at the factory.
There is a post office near the house.
Types of Nouns:
Common and Proper Nouns:
- Common nouns refer to general, ordinary things or entities (e.g., dog, city).
- Proper nouns refer to specific, individual entities (e.g., Max, New York).
Singular and plural nouns:
- Singular nouns refer to one person, place, thing, or idea (e.g., book, car).
- Plural nouns refer to more than one person, place, thing, or idea (e.g., books, cars).
Countable and Uncountable Nouns:
- Countable nouns can be counted and have both singular and plural forms (e.g., chair, book).
- Uncountable nouns cannot be counted individually and usually don’t have plural forms (e.g., water, happiness).
Abstract and Concrete Nouns:
- Abstract nouns refer to intangible concepts, feelings, or qualities (e.g., love, honesty).
- Concrete nouns refer to tangible, physical objects or entities (e.g., table, tree).
Collective and Possessive Nouns:
- Collective nouns refer to groups or collections of people or things (e.g., family, team).
- Possessive nouns indicate ownership or possession of something (e.g., John’s car, the dog’s leash).
Material Nouns:
- Material nouns refer to substances or materials from which things are made (e.g., wood, metal).
Compound Nouns:
- Compound nouns are formed by combining two or more words to create a new noun (e.g., toothbrush, breakfast).
Noun Sentences:
(nouns are highlighted.)
- The sun rose early, casting a warm glow over the city.
- She packed her suitcase with clothes and toiletries for the trip.
- His favourite book sat on the shelf, waiting to be read again.
- The river flowed gently, its waters reflecting the vibrant colours of the sunset.
- We enjoyed a delicious dinner of grilled steak and fresh salad.
- The children played with their new toys in the backyard.
- His laptop contained all of his important documents and files.
- The mountain stood tall against the backdrop of the clear blue sky.
- She wore a stunning dress to the party, attracting compliments from everyone.
- The sound of music filled the air as the band played on stage.
- We admired the intricate details of the ancient paintings in the museum.
- The doctor prescribed medication to help alleviate her symptoms.
- The moon shone brightly, illuminating the night sky with its soft light.
- The dog wagged its tail eagerly, excited to go for a walk.
- We gathered around the fireplace, sharing stories and laughter.
- The teacher explained the lesson using diagrams and examples on the whiteboard.
- The smell of freshly baked bread wafted through the air from the bakery.
- He carefully placed the fragile vase on the table, making sure it wouldn’t topple over.
- The rain fell steadily, creating a soothing rhythm on the roof.
- She received a bouquet of colourful flowers on her birthday, brightening up her day.
Nouns in Singular and Plural form
The Types of the English Pronouns